Description
Styrene: A Versatile Building Block of Modern Life
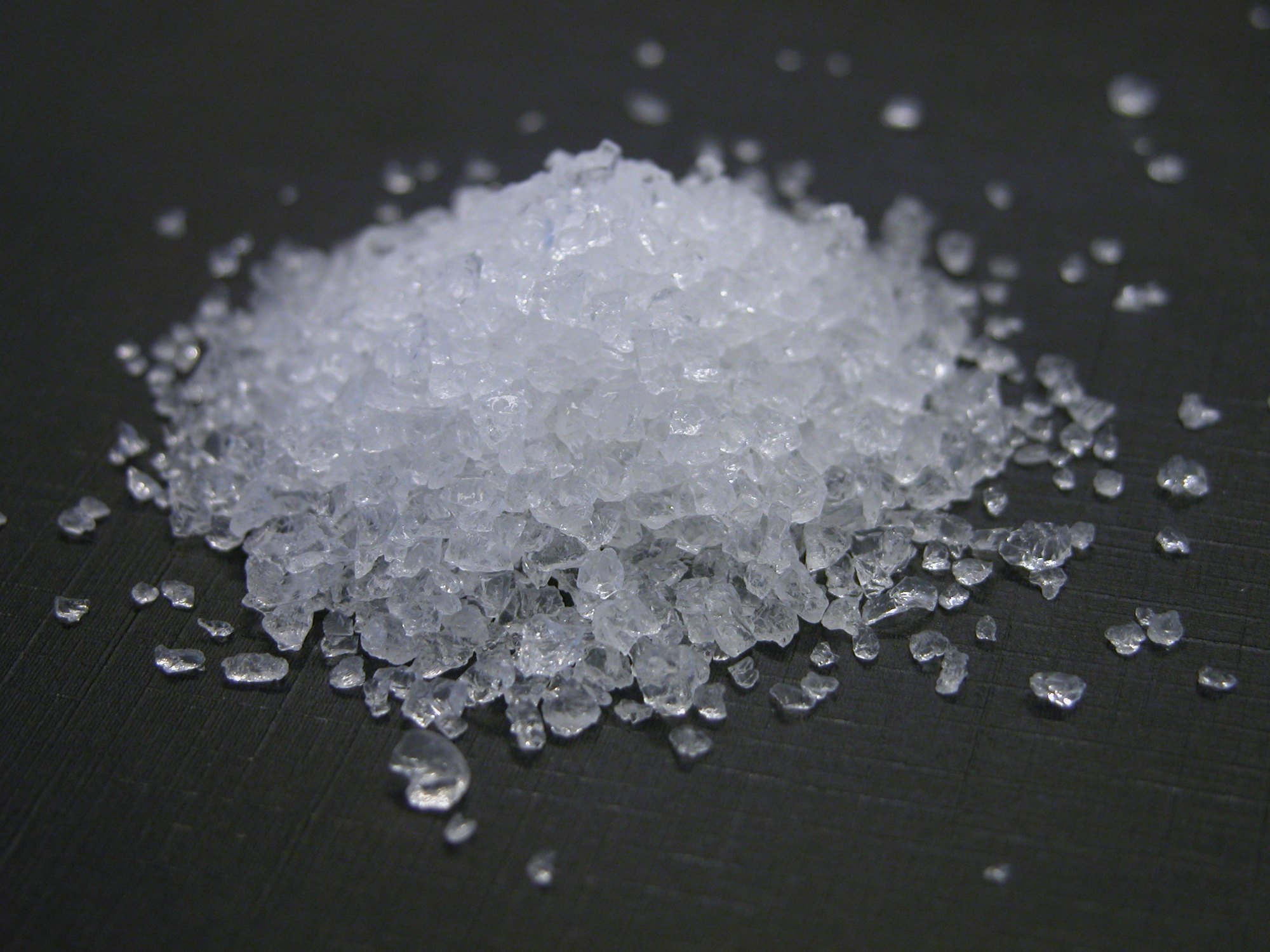
Styrene, a colorless, oily liquid with a characteristic aromatic odor, might not be a household name, but it’s a crucial chemical intermediate responsible for a vast array of products we use daily. From the foam cups you enjoy your coffee in to the tires on your car, styrene plays a vital role in modern life.
What is Styrene?
Styrene, also known as vinylbenzene, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C8H8. It’s a derivative of benzene, where one hydrogen atom is replaced by a vinyl group (CH=CH2). This seemingly simple structure gives styrene its reactive nature, making it a valuable building block in the polymer industry.
The Polymer Powerhouse:
The primary use of styrene is in the production of polymers, most notably polystyrene. This familiar plastic comes in various forms:
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS): This lightweight, rigid foam is commonly used for insulation, packaging (think of those ubiquitous white foam containers), and disposable cups. Its excellent insulation properties and cost-effectiveness make it ideal for these applications.
- General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS): A clear, brittle plastic often found in food packaging, CD cases, and laboratory ware.
- High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS): Formed by adding rubber to polystyrene, HIPS is much tougher and more resistant to impact. It’s used in refrigerator liners, appliance housings, and automotive parts.
Beyond polystyrene, styrene is also a key component in other important polymers:
- Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR): A synthetic rubber used extensively in tires, shoe soles, and other applications requiring durability and elasticity.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): A strong, rigid plastic known for its impact resistance and heat resistance. It’s commonly found in LEGO bricks, computer housings, and automotive dashboards.
- Unsaturated Polyester Resins: These resins are used in combination with glass fibers to create durable, lightweight composites for boats, car bodies, and construction materials.
Production and Manufacturing:
Styrene is primarily produced through the dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene. This process involves heating ethylbenzene in the presence of a catalyst, removing hydrogen to form styrene. The majority of ethylbenzene is itself produced from the reaction of benzene and ethylene. These processes are typically carried out in large-scale chemical plants due to the hazardous nature of the materials involved.
Safety Considerations:
While styrene is a valuable industrial chemical, it’s essential to understand the associated safety concerns:
- Exposure Hazards: Short-term exposure to high concentrations of styrene can cause irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat. Prolonged exposure can affect the central nervous system, leading to headaches, fatigue, and dizziness.
- Flammability: Styrene is a flammable liquid and should be handled with care in well-ventilated areas.
- Environmental Concerns: Styrene can persist in the environment and may pose risks to aquatic life. Responsible waste management and recycling efforts are crucial to minimize environmental impact.
Looking Ahead:
The demand for styrene is expected to continue growing, driven by the ever-increasing need for plastics, rubbers, and other polymer-based materials. Ongoing research is focused on developing more sustainable production methods, including using renewable feedstocks and improving energy efficiency. Furthermore, efforts are being made to develop biodegradable or recyclable alternatives to styrene-based polymers to address environmental concerns.
In Conclusion:
Styrene, though often unseen, plays a critical role in the modern world. Its versatility as a chemical building block has enabled the creation of a wide range of products that improve our lives in countless ways. As we continue to innovate and address environmental concerns, the future of styrene will likely involve more sustainable production methods and the development of eco-friendly alternatives, ensuring its continued relevance in a rapidly changing world.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.