Description
Sodium Nitrite: More Than Just a Preservative
Sodium nitrite (NaNO2) is a chemical compound that often sparks both interest and concern. While known primarily for its role in food preservation, particularly in cured meats, sodium nitrite has a range of applications in various industries, from medicine to manufacturing. Understanding its properties, benefits, and potential risks is crucial to appreciating its complex story.
The Science Behind Sodium Nitrite
Sodium nitrite is an inorganic salt composed of sodium, nitrogen, and oxygen. In food, it acts as a curing agent, contributing to the characteristic pink color and flavor of cured meats like bacon, ham, and hot dogs. More importantly, it inhibits the growth of Clostridium botulinum, the bacteria responsible for botulism, a potentially fatal form of food poisoning. This antimicrobial property is a vital reason for its use in the meat processing industry.
Benefits Beyond Preservation:
Beyond food preservation, sodium nitrite boasts several other significant applications:
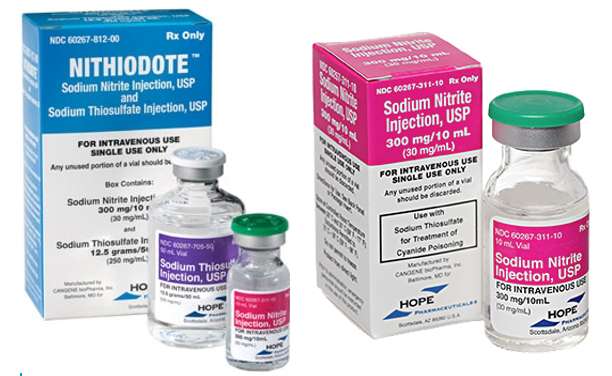
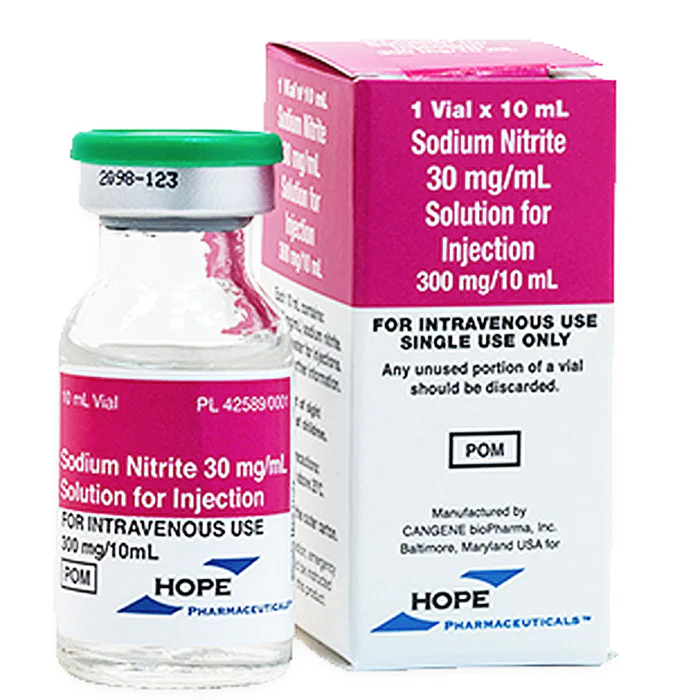
- Medicine: In medicine, sodium nitrite is used as an antidote for cyanide poisoning. It works by converting hemoglobin in the blood to methemoglobin, which then binds to cyanide, allowing it to be safely excreted from the body. It is also used to treat certain heart conditions by relaxing blood vessels and improving blood flow.
- Manufacturing: Sodium nitrite is used in the manufacturing of dyes, rubber chemicals, and explosives. It plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions and industrial processes.
- Photography: In photography, it’s used as a reagent in developing solutions.
Addressing the Concerns: Nitrites and Health
Despite its benefits, sodium nitrite has faced scrutiny due to its potential health risks. The primary concern revolves around its ability to react with amines in the stomach to form nitrosamines. Some nitrosamines are known carcinogens. This risk is amplified when cured meats are cooked at high temperatures, increasing nitrosamine formation.
However, the presence of vitamin C and other antioxidants in food can inhibit nitrosamine formation, mitigating the risk. Furthermore, regulations in many countries limit the amount of sodium nitrite allowed in food products.
Minimizing Risks and Making Informed Choices:
Consumers can take steps to minimize potential risks associated with sodium nitrite consumption:
- Choose products with added antioxidants: Look for cured meats that contain vitamin C (ascorbic acid) or other antioxidants, which can help prevent nitrosamine formation.
- Cook cured meats at lower temperatures: Avoid high-heat cooking methods like frying or grilling, which can increase nitrosamine levels.
- Consume a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides ample antioxidants that can further reduce the risks associated with nitrite consumption.
- Moderation is key: As with any food group, consuming cured meats in moderation is a good practice.
The Verdict: A Necessary Evil or a Valuable Tool?
Sodium nitrite remains a controversial compound. While concerns about its potential health risks are valid, its benefits in food preservation and medicine are undeniable. It’s a complex substance with a critical role to play in various industries.
Ultimately, understanding the science behind sodium nitrite, recognizing its potential benefits and risks, and making informed consumption choices are crucial. Instead of viewing it as simply a “necessary evil,” a balanced perspective acknowledges its value while emphasizing the importance of moderation and responsible application. By staying informed and making conscious choices, we can navigate the complexities of sodium nitrite and its place in our lives.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.