Description
Polycarbonate: The Versatile Plastic Shaping Our Modern World
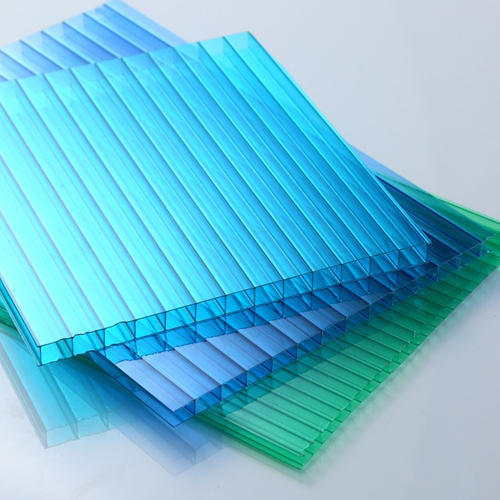
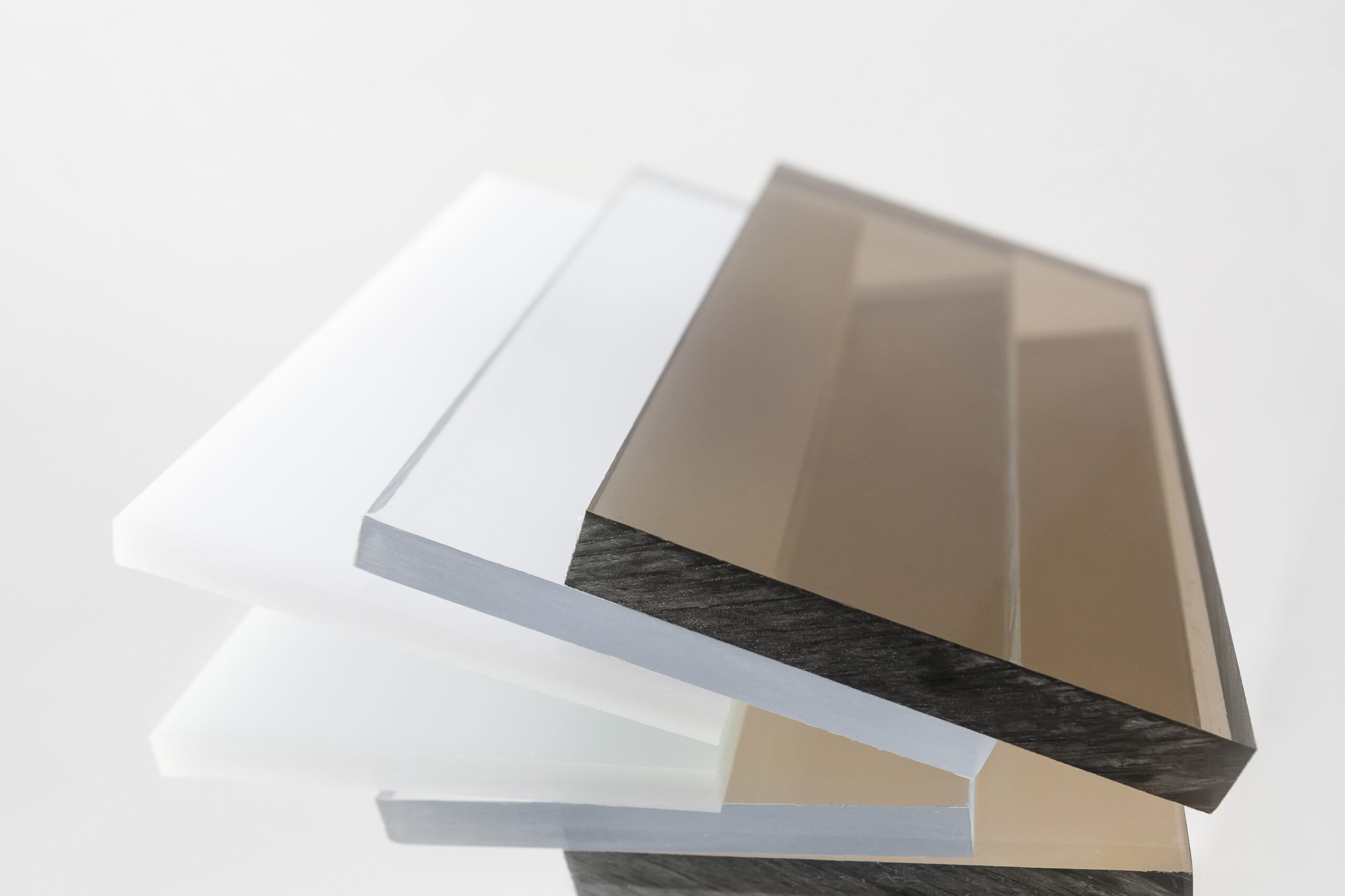
Polycarbonate (PC) is a robust and versatile thermoplastic polymer that has become indispensable in a wide range of industries, from construction and automotive to electronics and healthcare. Its unique combination of high impact resistance, optical clarity, heat resistance, and dielectric properties makes it a superior alternative to materials like glass, acrylic, and even some metals in numerous applications.
What Makes Polycarbonate So Special?
The magic of polycarbonate lies in its chemical structure. Its repeating units are linked by carbonate groups, which create a strong, rigid structure with exceptional durability. This results in a material that boasts:
- Exceptional Impact Resistance: Arguably its most defining characteristic, polycarbonate is incredibly resistant to shattering and cracking. It’s often described as being “virtually unbreakable.”
- Optical Clarity: High-quality polycarbonate offers excellent transparency, allowing for clear visibility and light transmission comparable to glass.
- High Heat Resistance: Polycarbonate can withstand high temperatures without deforming, making it suitable for applications under heat stress.
- Lightweight: Compared to glass and many metals, polycarbonate is significantly lighter, offering weight savings in structural applications.
- UV Resistance: Some polycarbonate grades are formulated with UV stabilizers to prevent degradation and yellowing from prolonged sun exposure.
- Dimensional Stability: Polycarbonate maintains its shape and size even under varying temperature and humidity conditions.
- Design Flexibility: It can be easily molded and formed into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs and applications.
Applications Across Industries:
The versatility of polycarbonate has led to its widespread adoption in various sectors:
- Construction: Polycarbonate sheets are used for roofing, skylights, transparent walls, greenhouses, and sound barriers. Their impact resistance and weather resistance make them ideal for these applications.
- Automotive: Polycarbonate finds its way into headlight lenses, dashboards, interior trim, and even some body panels. Its high impact resistance contributes to vehicle safety.
- Electronics: From smartphone cases and laptop housings to circuit boards and connectors, polycarbonate provides durable protection for electronic components.
- Healthcare: Polycarbonate is used in medical devices, surgical instruments, and dialysis equipment due to its biocompatibility and sterilizability.
- Safety and Protective Gear: Safety glasses, face shields, riot shields, and helmets rely on polycarbonate’s impact resistance to provide crucial protection.
- Optical Media: Polycarbonate was once the dominant material for CDs and DVDs, leveraging its optical clarity and uniformity.
- Food and Beverage: Food storage containers, water bottles, and baby bottles are often made from polycarbonate because it’s durable and can be cleaned easily.
Advantages Over Alternatives:
Polycarbonate offers several advantages over traditional materials:
- Glass: Polycarbonate is significantly more impact-resistant than glass, making it safer and more durable in applications where breakage is a concern.
- Acrylic: While acrylic is also transparent, polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and heat resistance.
- Metals: Polycarbonate is lighter than most metals, offering weight savings and design flexibility, particularly in automotive and aerospace applications.
Sustainability and the Future of Polycarbonate:
While traditionally produced from bisphenol A (BPA), concerns about BPA’s potential health effects have led to the development of alternative polycarbonate formulations. Furthermore, research is underway to develop more sustainable production methods and improve the recyclability of polycarbonate.
The future of polycarbonate looks promising. As technology advances and new applications emerge, the demand for this versatile material is expected to continue growing. Its unique properties and ongoing innovations will continue to shape our modern world in countless ways.
In conclusion, polycarbonate is a remarkable thermoplastic polymer that offers a compelling combination of strength, clarity, and versatility. Its widespread adoption across diverse industries is a testament to its unique properties and its ability to outperform traditional materials in a variety of demanding applications. As research continues to improve its sustainability and explore new formulations, polycarbonate is poised to remain a key material in shaping our future.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.