Description
Galvanized Hollow Sections: Strength and Corrosion Resistance for Modern Construction
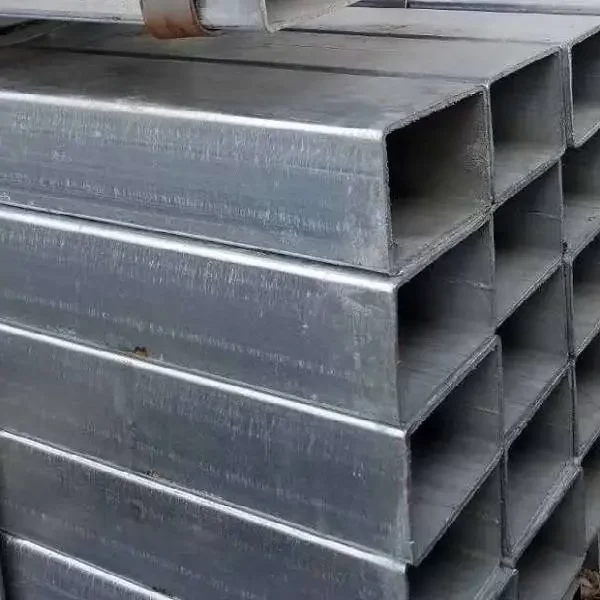
Galvanized Hollow Sections (GHS) are rapidly becoming a preferred choice for a wide range of construction and manufacturing applications, offering a compelling combination of strength, versatility, and long-term corrosion protection. These hollow structural sections, coated with a protective layer of zinc, are transforming the way we build, offering significant advantages over traditional materials and uncoated steel alternatives.
What are Galvanized Hollow Sections?
Hollow sections, as the name suggests, are steel tubes with a hollow core. They come in various shapes, including square, rectangular, circular, and elliptical, each offering unique structural properties. Galvanized Hollow Sections take this inherent strength and versatility a step further by applying a zinc coating through a process called galvanization.
The Power of Galvanization: Fighting Corrosion
The primary benefit of using GHS is their exceptional resistance to corrosion. Galvanization creates a barrier between the steel and the environment, preventing rust and degradation. This protection is achieved through two key mechanisms:
- Barrier Protection: The zinc coating physically shields the underlying steel from exposure to moisture, oxygen, and other corrosive elements.
- Sacrificial Protection: Even if the zinc coating is scratched or damaged, the zinc acts as a sacrificial anode. It corrodes preferentially, protecting the steel underneath. This “galvanic action” extends the lifespan of the GHS significantly, often for decades, even in harsh environments.
Advantages of Using Galvanized Hollow Sections:
The inherent benefits of GHS translate into tangible advantages for builders, manufacturers, and end-users:
- Extended Lifespan: The galvanization process dramatically increases the lifespan of the steel structure, reducing the need for frequent repairs and replacements. This translates into lower lifecycle costs.
- Reduced Maintenance: With its superior corrosion resistance, GHS require minimal maintenance, saving time and resources spent on painting or other protective measures.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Despite their hollow core, GHS offer a high strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for structural applications where weight is a concern. This can lead to savings in material and transportation costs.
- Versatility: GHS are available in a wide range of sizes, shapes, and thicknesses, making them suitable for diverse applications.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Depending on the galvanization process, GHS can offer a visually appealing surface finish, eliminating the need for additional coatings in some applications.
- Sustainability: The long lifespan of GHS reduces the need for frequent replacements, minimizing waste and conserving resources. Moreover, steel is a recyclable material, contributing to a more sustainable construction industry.
Applications of Galvanized Hollow Sections:
The combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and versatility makes GHS suitable for a wide range of applications, including:
- Structural Frameworks: Used extensively in building construction for columns, beams, and trusses, especially in coastal areas or industrial environments.
- Bridges and Infrastructure: Ideal for bridge supports, railings, and other infrastructure components prone to corrosion.
- Fencing and Guardrails: Providing durable and low-maintenance fencing and guardrails in various settings.
- Agricultural Structures: Used in barns, sheds, and other agricultural buildings where resistance to the elements is crucial.
- Automotive Industry: Employed in chassis components and other structural elements in vehicles.
- Signage and Lighting Poles: Offering stable and corrosion-resistant support for signs and lighting fixtures.
- Material Handling Equipment: Used in the construction of conveyors, racks, and other material handling systems.
Choosing the Right Galvanized Hollow Section:
Selecting the appropriate GHS for a specific application requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Load Requirements: Determine the structural loads that the section will need to bear.
- Environmental Conditions: Assess the level of corrosion exposure.
- Size and Shape: Choose the appropriate dimensions and shape to meet the design requirements.
- Galvanization Process: Consider the different galvanization methods and choose the one that offers the desired level of protection and finish.
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the GHS comply with relevant industry standards and regulations.
Conclusion:
Galvanized Hollow Sections represent a significant advancement in construction materials, offering a compelling combination of strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Their versatility and long lifespan make them a cost-effective and sustainable choice for a wide range of applications. As the demand for durable and low-maintenance structures continues to grow, GHS are poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of construction and manufacturing. By understanding their benefits and applications, engineers, architects, and builders can leverage the power of GHS to create safer, more sustainable, and longer-lasting structures.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.