Description
Ferric Nitrate: A Versatile Chemical Compound with Diverse Applications
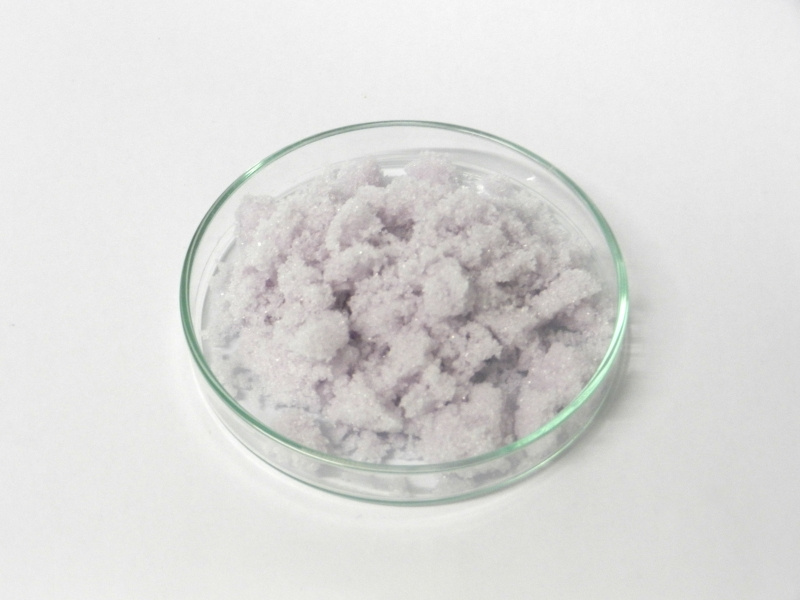
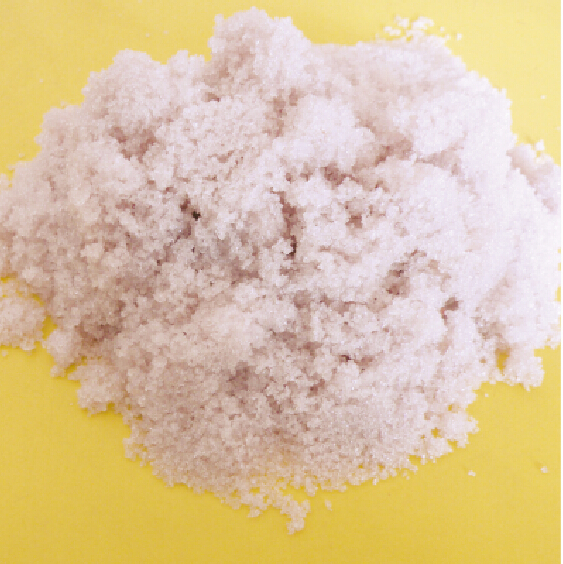
Ferric nitrate, with the chemical formula Fe(NO₃)₃, is an inorganic compound commonly encountered in the form of its nonahydrate, Fe(NO₃)₃·9H₂O. This pale purple, crystalline solid is a versatile chemical with a range of applications across various industries, from water treatment to analytical chemistry.
Properties and Characteristics:
Ferric nitrate is deliquescent, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air. This contributes to its ease of dissolution in water, forming acidic solutions. The compound is a strong oxidizing agent and reacts with many organic compounds, potentially leading to combustion or explosion under specific conditions. It’s important to handle ferric nitrate with caution, following appropriate safety protocols.
Key Applications:
Ferric nitrate’s diverse applications stem from its properties as a source of ferric ions (Fe³⁺) and its oxidative capabilities. Here’s a look at some of its prominent uses:
- Water Treatment: Ferric nitrate is widely used as a coagulant in water and wastewater treatment. It helps to remove suspended solids and impurities by causing them to clump together and settle out of the water. This process improves water clarity and reduces the burden on filtration systems.
- Laboratory Reagent: In analytical chemistry, ferric nitrate is used as a reagent in various tests and procedures. One notable application is in the detection of tannins and phenols, where it forms colored complexes upon reaction. It’s also used in the etching of metals and in the preparation of other chemical compounds.
- Catalysis: Ferric nitrate can act as a catalyst in certain organic reactions, promoting the formation of desired products. Its catalytic activity is often related to its ability to facilitate electron transfer and oxidation processes.
- Mordant in Dyeing: In the textile industry, ferric nitrate acts as a mordant, helping to fix dyes onto fabrics. It forms complexes with the dye molecules, making them more resistant to washing and fading.
- Animal Feed Supplement: In some cases, ferric nitrate is used as a source of iron in animal feed supplements, particularly for livestock that may have iron deficiencies.
- Electronics Industry: Ferric nitrate finds applications in the electronics industry, mainly for etching printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other microelectronic devices.
Safety Considerations:
While a versatile chemical, ferric nitrate requires careful handling. As a strong oxidizing agent, it can react violently with combustible materials. It is also corrosive and can cause skin and eye irritation. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, safety goggles, and a lab coat, should always be worn when handling this chemical.
Conclusion:
Ferric nitrate is a valuable chemical compound with a wide range of applications across various industries. Its properties as a coagulant, oxidizing agent, and catalyst make it essential in water treatment, analytical chemistry, and other fields. However, it is important to handle ferric nitrate with care, following proper safety procedures to avoid potential hazards. As research continues and technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovative uses for this versatile chemical in the future.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.