Description
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE): The Flexible Workhorse of the Plastics World
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its flexibility, resilience, and relative affordability. Often found in familiar everyday items, LDPE plays a significant role in various industries, from packaging and agriculture to construction and consumer goods. This article delves into the properties, applications, and environmental considerations surrounding this versatile material.
What is LDPE?
LDPE is a type of polyethylene derived from the polymerization of ethylene. Unlike its denser counterpart, HDPE (high-density polyethylene), LDPE has a branched structure. This branched structure prevents the polymer chains from packing tightly together, resulting in:
- Lower density: Hence the name “low-density.”
- Greater flexibility: Making it pliable and easy to mold.
- Lower tensile strength: Less resistant to tearing and stretching compared to other plastics.
- Lower melting point: Easier to melt and process.
- Chemical resistance: Resistant to acids, bases, and alcohols, but less resistant to oils and hydrocarbons.
- Good electrical insulation: Suitable for electrical applications.
Applications of LDPE: Everywhere You Look
LDPE’s unique properties make it a valuable material in a vast range of applications, including:
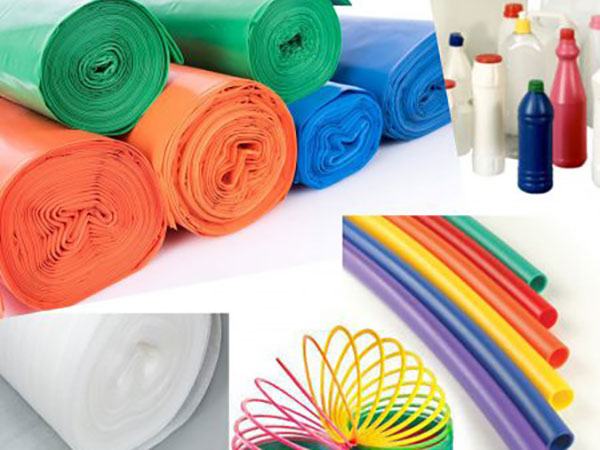
- Packaging: LDPE is a staple in food packaging, used for bread bags, produce bags, shrink wrap, and flexible packaging films. Its moisture resistance and flexibility are crucial for preserving the freshness and integrity of products.
- Agriculture: Agricultural films, greenhouse covers, and irrigation pipes benefit from LDPE’s flexibility, weather resistance, and transparency (when required). These applications help protect crops, regulate growing environments, and deliver water efficiently.
- Construction: LDPE is utilized in construction for vapor barriers, geomembranes for lining landfills, and temporary protective sheeting. Its low cost and resistance to water and chemicals make it a practical choice.
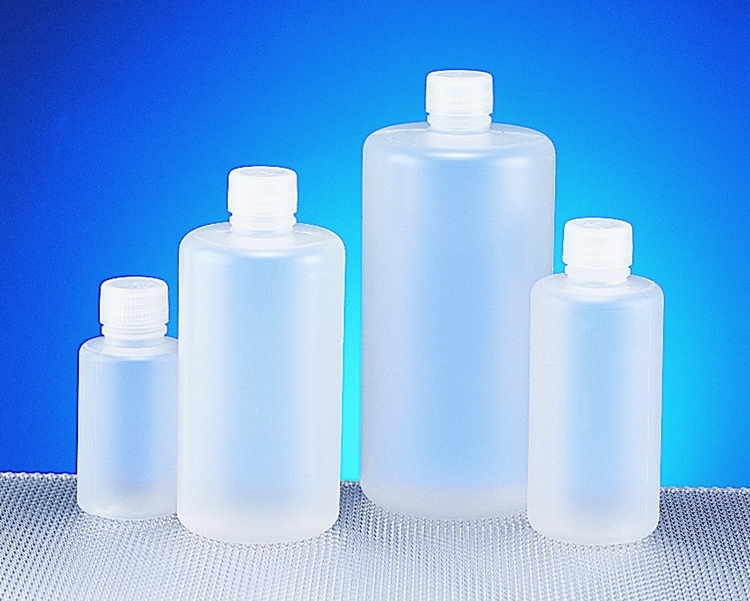
- Consumer Goods: From squeezable bottles for condiments and lotions to plastic shopping bags and toys, LDPE’s flexibility, ease of shaping, and low cost make it suitable for a multitude of consumer products.
- Wire and Cable Insulation: LDPE’s excellent electrical insulation properties make it a common choice for insulating wires and cables, ensuring safety and preventing electrical leakage.
Advantages of Using LDPE:
- Cost-effective: Relatively inexpensive compared to other polymers.
- Flexible and pliable: Easy to mold and shape into various forms.
- Moisture resistant: Protects packaged goods from dampness and spoilage.
- Chemical resistant: Resists degradation from many common chemicals.
- Good electrical insulator: Suitable for electrical applications.
- Easy to process: Can be easily molded and extruded.
Environmental Considerations:
While LDPE is a widely used and valuable material, its environmental impact is a significant concern.
- Recyclability: LDPE is recyclable, but recycling rates remain relatively low compared to other plastics. Improved collection and sorting infrastructure are crucial for increasing recycling rates.
- Degradation: LDPE is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, contributing to plastic pollution.
- Production Emissions: The production of LDPE, like other plastics, involves energy-intensive processes that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Moving Towards a More Sustainable Future:
Addressing the environmental challenges associated with LDPE requires a multi-pronged approach:
- Promoting recycling: Investing in better recycling infrastructure, increasing public awareness about the importance of recycling, and encouraging the use of recycled LDPE in new products.
- Developing biodegradable alternatives: Researching and developing biodegradable or compostable alternatives to LDPE for specific applications, particularly those with a high risk of environmental contamination.
- Reducing plastic consumption: Encouraging consumers to reduce their reliance on single-use plastics, promoting reusable alternatives, and supporting initiatives that minimize plastic waste.
- Improving production processes: Optimizing LDPE production processes to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion:
Low-density polyethylene is a remarkable material that has transformed countless industries through its versatility and affordability. However, responsible usage and a commitment to sustainable practices are essential to mitigate its environmental impact. By prioritizing recycling, exploring alternative materials, and reducing plastic consumption, we can harness the benefits of LDPE while minimizing its negative effects on the planet. As research and innovation continue to push the boundaries of material science, the future of LDPE, and plastics in general, will depend on our collective commitment to a more sustainable and circular economy.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.