Description
Understanding Ethylene Oxide: Uses, Safety, and Environmental Concerns
Introduction
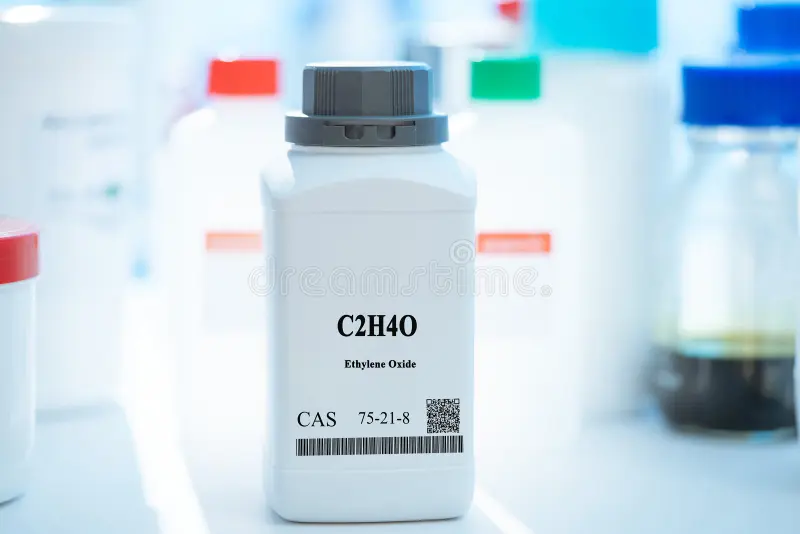
Ethylene oxide (C2H4O) is a colorless gas with a sweet odor that plays a crucial role in various industrial applications. As a key intermediate in the production of antifreeze, plastics, and chemicals, it has become an indispensable part of modern manufacturing processes. However, while its utility is vast, ethylene oxide also poses significant health and environmental risks that necessitate careful handling and regulation. This article explores the uses, safety aspects, and environmental implications of ethylene oxide.
What is Ethylene Oxide?
Ethylene oxide is a cyclic ether and a highly reactive compound. It was first synthesized in 1859 by the chemist Charles-Adolphe Wurtz. Since then, its applications have grown exponentially, particularly in the production of ethylene glycol and other chemicals. Ethylene glycol, in turn, is widely used in automotive antifreeze formulations, polyester fibers, plastics, and as a solvent.
Uses of Ethylene Oxide
- Production of Ethylene Glycol: The primary use of ethylene oxide is in the manufacturing of ethylene glycol, which is essential for producing antifreeze and industrial coolants.
- Sterilization Agent: Ethylene oxide is extensively utilized in the sterilization of medical equipment and supplies, especially those that are sensitive to heat and moisture. Its ability to penetrate packaging materials makes it an effective method for ensuring sterility.
- Production of Surfactants: Ethylene oxide serves as a building block for various surfactants, which are compounds that reduce surface tension and are vital in products like detergents, emulsifiers, and wetting agents.
- Chemical Intermediates: It is used in the synthesis of several other chemicals, including ethoxylates, which find applications in personal care products, pharmaceuticals, and agricultural chemicals.
- Refrigerants: Ethylene oxide can be utilized in specialized refrigerants, particularly in applications requiring low temperatures.
Safety Considerations
While ethylene oxide is a valuable compound, it is essential to recognize the associated health and safety risks. It is classified as a potential human carcinogen by agencies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Acute exposure can lead to respiratory irritation, headaches, nausea, and in severe cases, neurological impairment. Long-term exposure has been linked to reproductive issues and cancer development.
Given these risks, stringent safety measures are necessary when handling ethylene oxide. Industries that utilize this compound must adhere to comprehensive safety protocols, which include:
- Proper Ventilation: Ensuring adequate airflow in workspaces to minimize inhalation risks.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers should wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, goggles, and respirators.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implementing air quality monitoring systems to detect ethylene oxide concentrations.
Environmental Implications
Ethylene oxide’s reactivity also presents environmental concerns. When released into the atmosphere, it can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a key component of smog. Additionally, spills and leaks can contaminate soil and water sources. Regulatory agencies have set limits on emissions and usage to mitigate these impacts, emphasizing the importance of responsible management.
Efforts to recycle and repurpose ethylene oxide, as well as ongoing research into safer alternatives, aim to reduce environmental footprints while maintaining industrial efficacy.
Conclusion
Ethylene oxide is integral to a wide range of industrial processes, contributing to numerous everyday products and services. However, its potential health risks and environmental impact cannot be overlooked. As industries continue to rely on this compound, it is crucial to prioritize safety and environmental stewardship, ensuring that the benefits of ethylene oxide are realized without compromising human health or ecological integrity. Continued research, monitoring, and the development of safer alternatives are essential to achieving a balance between industrial needs and safety considerations.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.