Description
Bromine: A Multifaceted Element with a Surprising Impact
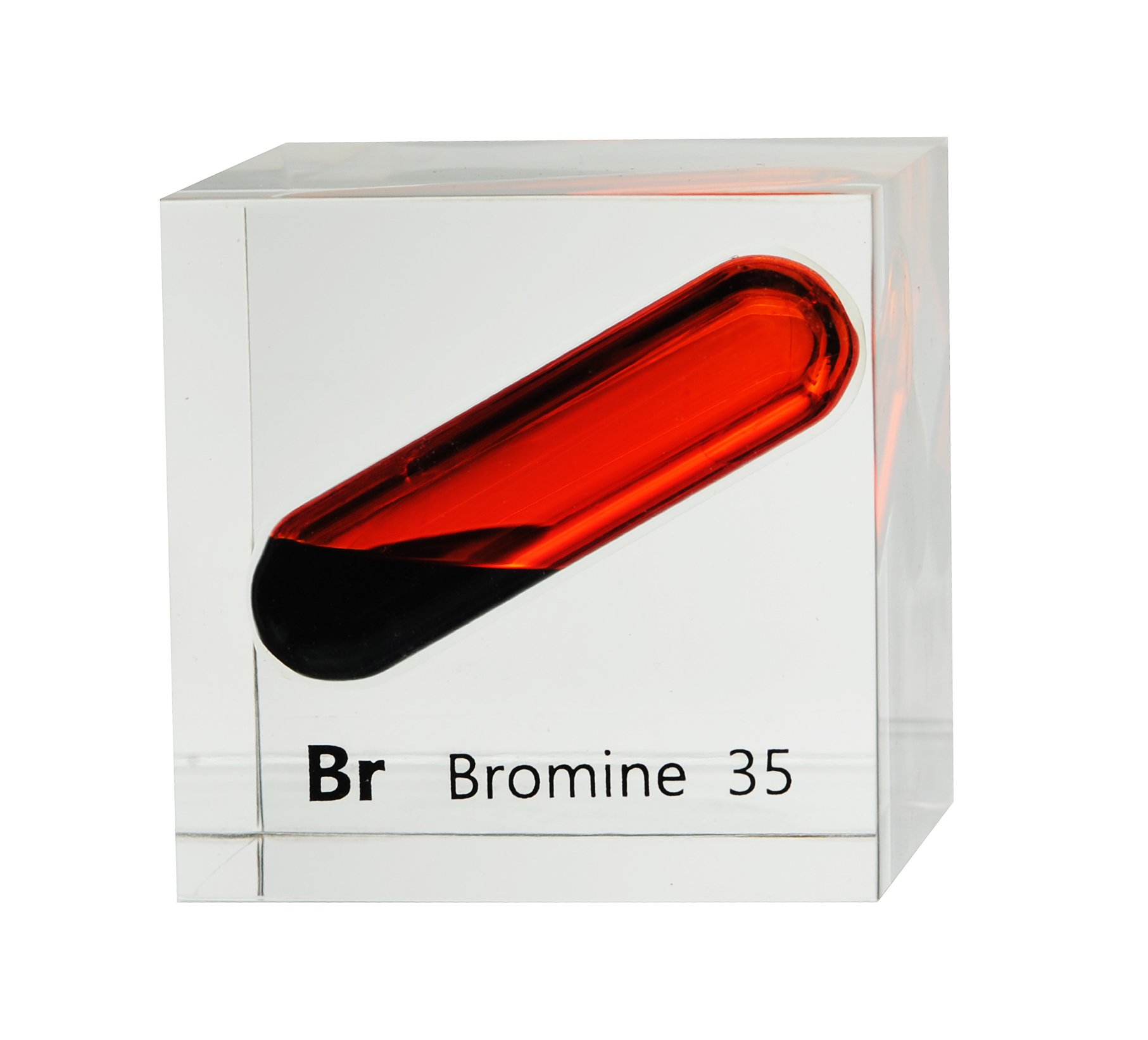
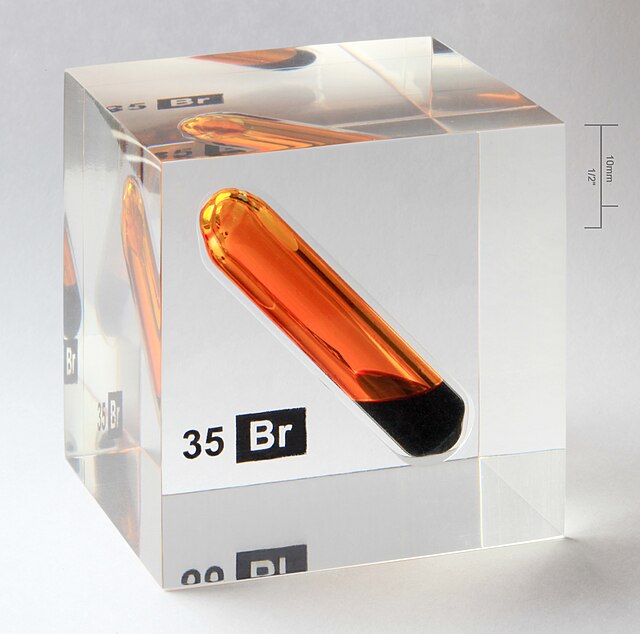
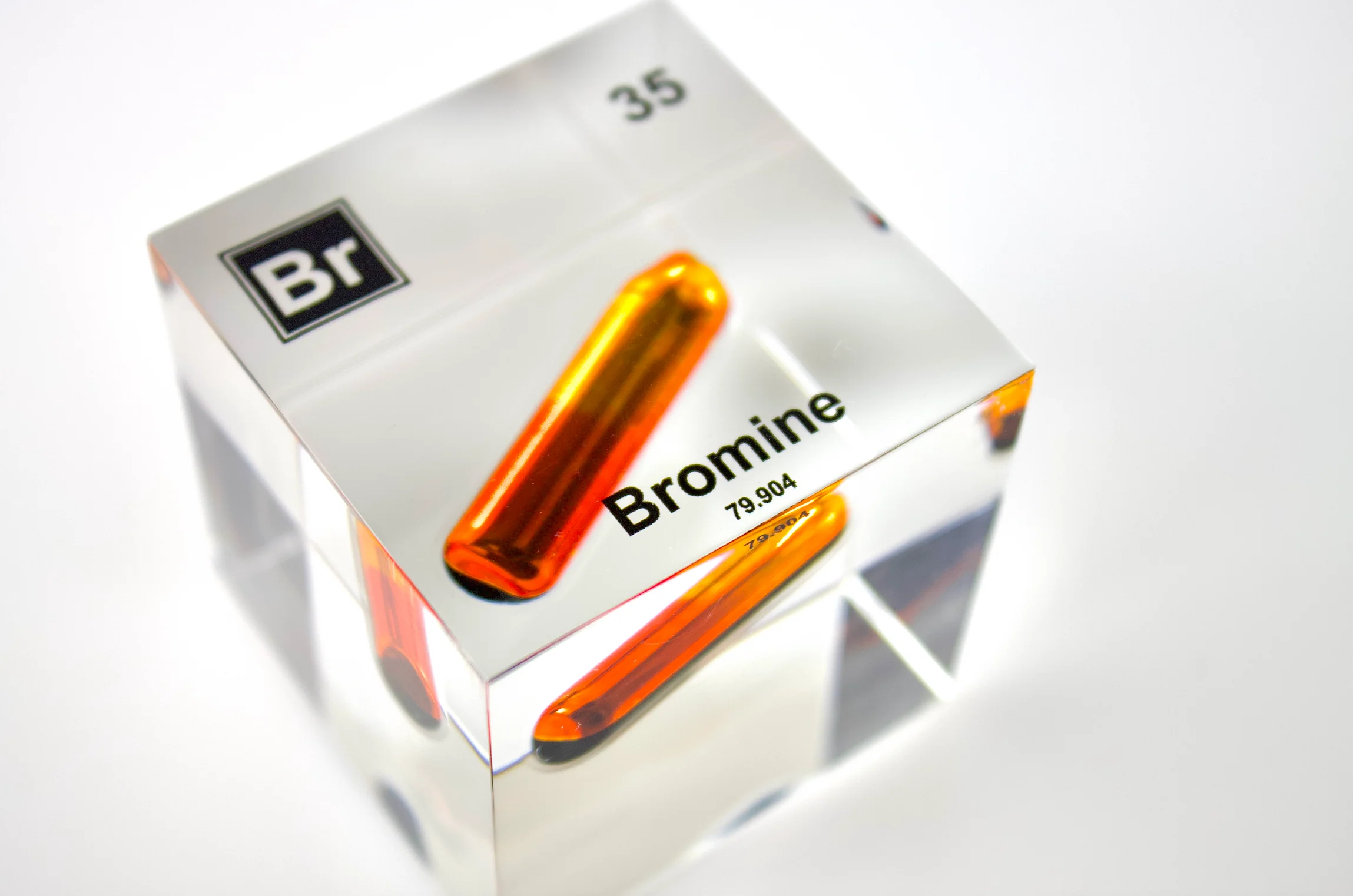
Bromine, a reddish-brown liquid at room temperature, is a fascinating element with a surprising range of applications and a checkered history. Belonging to the halogen family, known for their high reactivity, bromine plays a vital role in diverse fields, from agriculture and medicine to fire safety and even photography.
A Reactive Member of the Halogen Family:
Bromine (symbol Br, atomic number 35) is a nonmetal found in Group 17 (VIIA) of the periodic table. Its reactivity stems from its eagerness to gain an electron to complete its outer electron shell. This drive for stability makes it a powerful oxidizing agent, readily reacting with many elements and compounds.
This reactivity explains why free bromine is rarely found in nature. Instead, it exists primarily in the form of bromide salts, dissolved in seawater, salt lakes, and underground brine wells. The Dead Sea, for example, is a rich source of bromine.
From Photography to Fire Retardants: A Diverse Spectrum of Uses:
Bromine’s versatile properties have led to its widespread use across various industries:
- Agriculture: Methyl bromide, though now largely phased out due to environmental concerns, was once a widely used soil fumigant, effectively controlling pests and weeds in agricultural settings. While alternative fumigants are now preferred, bromine still plays a role in agricultural chemistry.
- Medicine: Bromides, such as potassium bromide, were historically used as sedatives and anticonvulsants. While these applications have largely been replaced by more modern drugs, bromine-containing compounds continue to be used in the development of new pharmaceuticals.
- Photography: Silver bromide, known for its sensitivity to light, was a key ingredient in traditional photographic film. Though digital photography dominates the market today, silver bromide remains relevant in specialized photographic applications.
- Fire Retardants: Brominated flame retardants (BFRs) are added to plastics, textiles, and electronic components to inhibit or delay combustion. While highly effective at preventing fires, some BFRs have raised environmental and health concerns, leading to ongoing research and development of safer alternatives.
- Water Treatment: Bromine can be used as a disinfectant, similar to chlorine, to control bacteria and algae in swimming pools and cooling towers. It’s often preferred in environments with high pH levels where chlorine is less effective.
- Drilling Fluids: Calcium bromide is used in drilling fluids in the oil and gas industry, increasing the density of the fluid and preventing blowouts.
Safety Considerations and Environmental Impact:
While bromine’s applications are numerous and beneficial, caution is necessary when handling it. Bromine is corrosive and can cause severe burns to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. Exposure to bromine vapor can lead to lung irritation and even pulmonary edema. Proper ventilation and protective equipment are crucial when working with bromine.
The environmental impact of bromine-containing compounds is also a concern. The use of methyl bromide as a fumigant contributed to ozone depletion. Furthermore, some BFRs can persist in the environment and bioaccumulate in living organisms, potentially causing adverse health effects. Responsible management and ongoing research are essential to mitigate these risks.
The Future of Bromine:
Despite the challenges, bromine remains an important element with a vital role to play in modern society. Ongoing research is focused on developing safer and more sustainable applications for bromine, including:
- Advanced Batteries: Bromine is being explored as a key component in advanced battery technologies, potentially leading to more efficient and energy-dense storage solutions.
- New Pharmaceuticals: Bromine is used in the development of new drugs to treat a variety of diseases, including cancer and infectious diseases.
- Environmentally Friendly Flame Retardants: Researchers are actively working to develop new bromine-containing flame retardants that are less persistent in the environment and pose less of a risk to human health.
Conclusion:
Bromine, with its unique properties and diverse applications, is a testament to the power and potential of the elements around us. While caution is necessary when handling it and its compounds, ongoing research and responsible management can ensure that bromine continues to contribute to advancements in various fields, shaping a safer and more sustainable future. From protecting crops to saving lives, bromine’s impact on our world is undeniable.













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.