Description
Conductive Inks: Printing the Future of Electronics
From flexible displays to smart clothing, the world of electronics is rapidly evolving, demanding innovative materials and fabrication techniques. One such technology, conductive inks, is poised to revolutionize how we design, manufacture, and interact with electronic devices. These inks offer a versatile and cost-effective alternative to traditional methods, opening up a plethora of possibilities for printed electronics.
What are Conductive Inks?
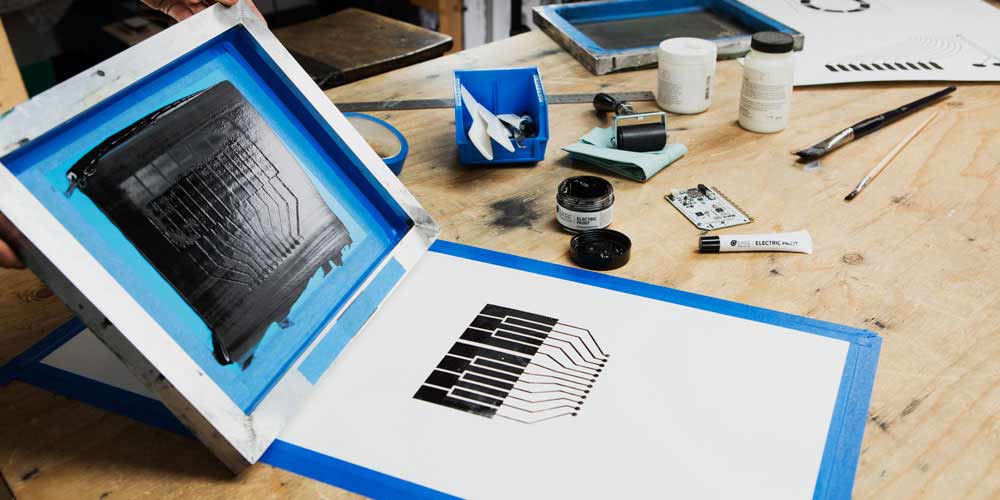
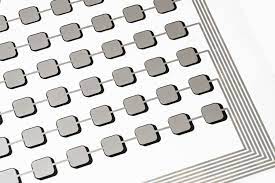
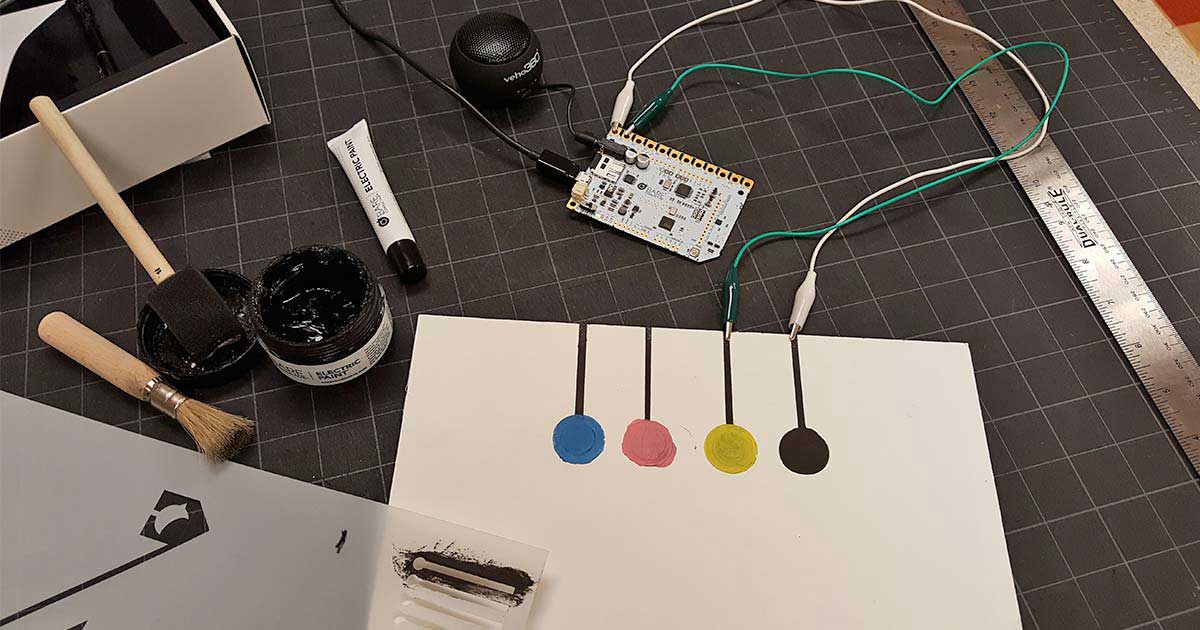
Conductive inks are specialized inks containing conductive particles, typically metals (like silver, copper, or gold), carbon-based materials (like carbon nanotubes or graphene), or conductive polymers. These particles are dispersed in a liquid carrier, allowing the ink to be printed onto a substrate using various printing methods like inkjet, screen printing, flexography, gravure, and aerosol jet printing. Once the ink is deposited and dried or cured, the conductive particles form a continuous network, enabling the flow of electricity.
Why are Conductive Inks Gaining Traction?
The appeal of conductive inks stems from their ability to address limitations of traditional electronic fabrication methods:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Printing is generally a faster and more efficient production method than etching, photolithography, and vacuum deposition, potentially reducing manufacturing costs.
- Flexibility and Conformability: Conductive inks can be printed on a wide range of substrates, including flexible materials like paper, plastic, and textiles. This enables the creation of flexible and wearable electronics that can conform to complex shapes.
- Rapid Prototyping: The ease of printing circuits allows for rapid prototyping and design iteration, accelerating the development cycle.
- Customization and Scalability: Printing technologies allow for highly customized designs and can be readily scaled for mass production.
- Sustainability: Compared to traditional fabrication processes, printing often generates less waste and consumes less energy, offering a more environmentally friendly alternative.
Applications of Conductive Inks:
The versatility of conductive inks has led to a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): Conductive inks can be used to create simple PCBs for low-power applications, eliminating the need for etching and drilling.
- Flexible Electronics: This is arguably the most exciting application area. Conductive inks are crucial for producing flexible displays, sensors, batteries, and wearable devices.
- RFID Tags: Conductive inks are used to print antennas for Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) tags, enabling item tracking and inventory management.
- Solar Cells: Conductive inks can be used as front and back electrodes in solar cells, improving their efficiency and reducing production costs.
- Touch Screens: Conductive inks are used to create transparent conductive films for touch screen displays.
- Sensors: Conductive inks can be used to create a variety of sensors, including pressure sensors, temperature sensors, and gas sensors.
- Smart Packaging: Integrating printed electronics into packaging allows for real-time monitoring of product conditions, such as temperature and humidity.
- Medical Devices: Conductive inks are finding use in medical sensors, electrodes for ECG/EEG monitoring, and drug delivery systems.
Challenges and Future Directions:
Despite their potential, conductive inks still face some challenges:
- Conductivity: The conductivity of printed traces is often lower than that of traditional copper traces. Research is focused on improving the conductivity of inks through the development of new materials and optimized printing processes.
- Durability: The mechanical and environmental stability of printed traces can be a concern, particularly in harsh environments. Improving the adhesion and resistance of inks to wear, chemicals, and humidity is crucial.
- Ink Formulation: Formulating inks with the right viscosity, surface tension, and stability is essential for reliable printing.
- Compatibility: Ensuring the compatibility of inks with different substrates and printing techniques is important for expanding the application range.
Looking ahead, the future of conductive inks is bright. Ongoing research and development are focused on:
- Developing new conductive materials: Exploring novel materials like metal nanowires, MXenes, and quantum dots to achieve higher conductivity and stability.
- Improving printing techniques: Optimizing printing parameters and developing new printing methods to enhance the resolution and uniformity of printed traces.
- Creating multi-functional inks: Developing inks with additional functionalities, such as sensing, energy harvesting, and self-healing properties.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI): Using AI to optimize ink formulations, predict printing performance, and automate the printing process.
Conclusion:
Conductive inks are transforming the landscape of electronics, offering a powerful and versatile tool for creating innovative devices and applications. As research and development continue to advance, conductive inks will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of electronics, enabling the creation of smarter, more flexible, and more sustainable technologies. The printing revolution is underway, and conductive inks are leading the charge.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.